- Germany 8
- Argentina 12
- Australia 1
- Austria 10
- Belgium 2
- Brazil 3
- Czech Republic 1
- Chile 2
- China 1
- Colombia 21
- South Korea 1
- Denmark 3
- Egypt 2
- Slovenia 1
- Spain 199
- Finland 3
- France 20
- Greece 4
- Holland 7
- Hungary 1
- India 1
- Iraq 1
- Ireland 1
- Italy 28
- Japan 11
- Mexico 15
- Norway 1
- Netherlands 2
- Peru 0
- Poland 3
- Portugal 5
- Puerto Rico 2
- UK 20
- Russia 1
- Syria 1
- Sri Lanka 1
- Sweden 4
- Switzerland 10
- Turkey 1
- Uruguay 1
- USA 48
- Venezuela 1
-
Juan Daniel Fullaondo – Publications
MOST IMPORTANT PUBLICATIONS.
During his professional career there are many works written about architecture and sculpture, important Spanish contemporary architects and books on poems. Here we will collect those made most significant.
They stand out among those publications as;
- 1968. Chillida. Madrid: Alfaguara
- 1969. The architecture and urbanism of the region and the environment of Bilbao I. Madrid: Alfaguara.
- 1971. Architecture and urbanism of the region and the environment of Bilbao II. Madrid: Alfaguara.
- 1972. Art, architecture and everything else. Madrid: Alfaguara.
- 1976. Oteiza and Chillida in the modern historiography of art. Bilbao: The great Basque encyclopedia.
- 1976. Jorge Oteiza sculptor. Madrid: Alfaguara.
- 1989. Composition of place.
- 1990. Oteiza. Double portrait.
- 1990. Composition of the place. The architecture between art and science. Madrid: Hermann Blume.
- 1991. Art, project and everything else: or an antidote to galliformes and Rams. Madrid: Kain.
- 1991. Twilight Laocoön. Conversations around Eduardo Chillida. Madrid: Kain.
- 1992. Zevi.
- 1993. Tribute to Oscarin and architectures of Bilbao.
- 1994. History of Spanish contemporary architecture. Looking back with some anger (sometimes). Madrid: Kain.
- 1996. Juan Daniel Fullaondo. Built work. Madrid, Munillaleria.
-
Juan Daniel Fullaondo – Websites
BIOGRAPHY AND INTERESTING LINKS.
- http://www.euskomedia.org/aunamendi/63309
- http://www.euskalnet.net/laviana/monografias/fullaondo.html
- http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/autor?codigo=77178
-
Juan Daniel Fullaondo – Projects
MAJOR PROJECTS.
During his professional career there are many works and projects, as well as a large number of works written about architecture and sculpture, important Spanish contemporary architects and books on poems. Here we will collect those made most significant.
His work is very broad and includes actions such as;
- 1966 – 1976. In these years he made, mainly, residential projects, which included the homes of neighborhood that was erected, in collaboration with Álvaro Líbano and Fernando Olabarría, in different municipalities vizcaínos: Bilbao, Getxo and very especially in Durango, where was Olabarria municipal architect. He also developed several projects summer apartment in the Mediterranean basin.
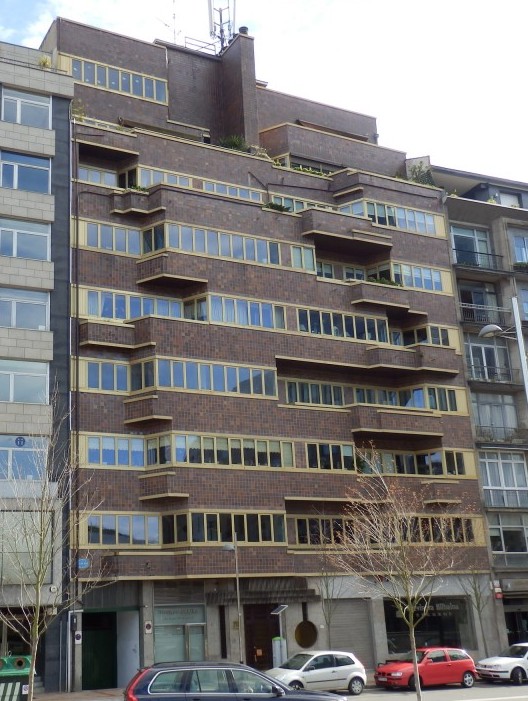
- 1965. The tenement house that held at the alameda Mazarredo in Bilbao, together with Olabarria, Fullaondo understood as a new path.
In the alameda Mazarredo in Bilbao tenement house. 1965.
- 1969 – 1972. Construction of eight school groups in collaboration with Olabarria and Lebanon, vizcaínos municipalities: Bilbao, Durango, Markina, Santurce and Zaratamo, in which was found a rationalistic neo attitude, and its recovery after a period of little activity.
- 1970 – 1972. Fullaondo urbanistic interventions include the Plaza Ezkurdi de Durango, in collaboration with Olabarria. In the words of the architect it is the most significant work of that time, and with which you feel most identified. Fullaondo proposed to build a bosque-plaza crossed by a river, It was articulated without axial ordinations and at different levels, around the old monument of Fray Juan de Zumárraga who adopted a semicircular form. The project was completed with other sculptures: a replica of the Mikeldi, other reused of Angel Ferrant, two made by itself, and by a great work of Eduardo Chillida, that finally is it did not consider.
Ezkurdi de Durango square. 1970-1972.
- 1970 – 1973. Single-family homes (as the home of the painter Rafael Canogar in Madrid) they are scarce in their production, already the architect he was not comfortable with this kind of projects due to problems originating.
- 1971. Neighborhood emergency units project, Along with Canogar and Antonio Fernández Alba, at the same time that it made other social housing projects.
- 1974 – 1976. He made different educational centres, cultural, sports and office buildings: as the disfigured European business bank in Bilbao in collaboration with Félix Iñiguez de Onzoño and José Luis Iñiguez de Onzoño.
- 1976. Housing and offices for the company GES in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria with Olabarria.
- 1972 – 1979. Several projects in collaboration with Juan Luis Candela and Fernando Perez Segura Alicante and Alcoy haven, with those who began their working relationship.
- 1981. The ambulatory Aspe.
- 1983. The National Center of Social Welfare of Madrid, along with Luis Arana and Germán Castro.
- 1983. Ciudad Real Social Information Center, along with Luis Arana and Germán Castro.
- 1985. The Centre of technical AIDS to disabled people of Parla, along with Luis Arana and Germán Castro.
- 1987. The asylum of elders of Getafe, along with Luis Arana and Germán Castro.
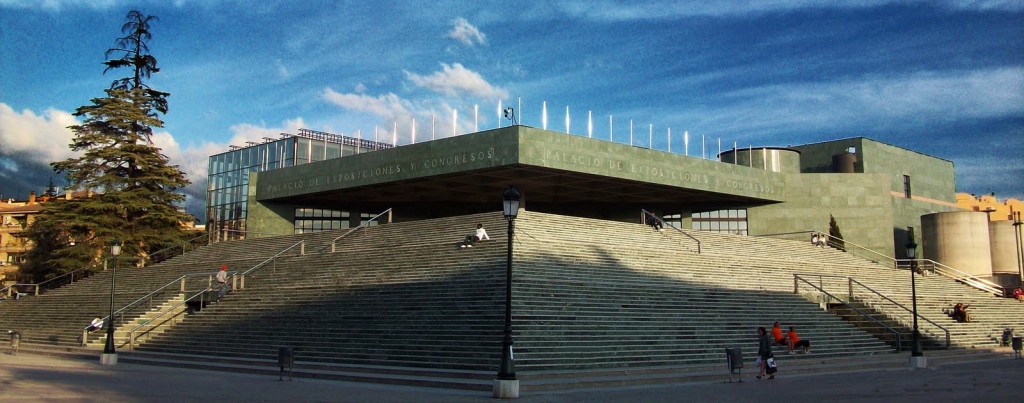
- 1984 – 1992. Palacio de Exposiciones y Congresos of Granada, one of the most important projects of that time, in collaboration with José Ibáñez Berble, María Jesús Muñoz and Over Aurp & Partners. With the building they wanted to create an independent body, Thanks to the exterior marble cladding had formed a large green mountain. While the interior, inspired by the Palace of Carlos V, It houses a multiplicity of spaces which highlights the glazed entrance.
Palacio de Exposiciones y Congresos de Granada. 1984-1992.
- 1990- 1996. The offices of the Madrid calle Almansa, one of the last works of Fullaondo, built in collaboration with Kevin Roche and José Luis González Cruz, as well as Darío Gazapo and María Teresa Muñoz. It's unit set of four organized grid-fronted office buildings around a square interior. The module becomes the key to solve both building exterior façade, as inside. Proportion of its volumes and the absence of ornament.
Offices of the Madrid calle Almansa. 1990-1996.
-
Juan Daniel Fullaondo – Biography
BIOGRAPHY.
Juan Daniel Fullaondo Errazu was born in Bilbao the 4 March 1936 and died in Madrid the 26 June 1994, fifty-eight years old.
Architect, teacher, writer and historian of architecture.
A student in the school of architecture of Madrid held his first work in the study of the Bilbao architects Manuel Galíndez and Jesús María Chapa, and after graduating in 1958 He began to collaborate with the study of the Navarrese architect based in Madrid, Francisco Javier Sáenz de Oiza, with whom he collaborated on several of his works as the circular schools of the town of Batan, the apartamentos-terrazas in Mallorca or the white towers of Madrid.
In 1962, at the age of 26 years old, He got the national Architecture Prize with a project of a theatre in the open air that was never erected.
Starting 1963 He opened his own Studio and began teaching at the school where he studied. In 1964 He presented his doctoral thesis, which dealt with the relationship between architecture and the music of Arnold Schoenberg and Boulezse. He obtained his doctorate at the school of Madrid with a thesis entitled: “Relationships between music and architecture through Arnold Schoemberg”, highlights the artistic conception - cultural of the author.
In the study of Oiza, Fullaondo met Juan Huarte navarro constructor, initiating a relationship that materialized in the construction of some projects in Madrid, as HISA offices (1965) where the architect was also responsible for furniture, and the defunct store “H furniture” (1965- 1966). The store is for Fullaondo his latest example of organic work, It is as well as the architect refers to the first phase of his work. This time they are also, one of the few orders for your family, the Pantheon Errazu in Derio (1964), the proposals submitted to the competitions of Palace of the Opera and Palace of exhibitions and congresses of Madrid (1964), or the Kursaal in San Sebastian (1965).
In 1966 He was appointed member of the Editorial Board of the magazine Architecture, and he married Paloma Buigas of Dalmau, with whom he had two sons: Diego and Maria, also architects.
Starting 1966 the architect notes a change in his work, more calm, based on a hardened language, gross that evokes the forms of the avant-garde Rationalist, a rationalist neo attitude which, in his view, was released by Oíza. It was a time of study of the architecture of the 1920s and 1930s, the work of the sculptor Jorge Oteiza, Minimal art, Conceptual and Land art, and interest in the work of Giorgio De Chirico. At this stage, away from the school of architecture, He made a greater number of buildings than in previous years, which meant a maturity and professionalism, accompanied by a greater pragmatism.
Addition of constructions, Juan Daniel Fullaondo is notable for being the author of some of the first papers that were published on contemporary Spanish architects.
From 1967 and up to 1972 He directed the architecture magazine New form. In 1976 He was appointed member of the International Committee of the magazine Architecture, in 1979 of the orientation Committee of Éditions de Montieur of Paris, and in 1985 He was invited by the ICOMOS (International Council on monuments and sites) UNESCO to be part of a Committee of experts in contemporary architecture.
Between 1969 and 1972 Fullaondo, in collaboration with Olabarria and Lebanon, He built eight different municipalities bizkaian school groups: Bilbao, Durango, Markina, Santurce and Zaratamo, in which was found a rationalistic neo attitude, and its recovery after a period of little activity. Fullaondo considered that schools, where was the culture protagonist, It would be advisable to insert an architectural cultural factor. It was in this case a reconsideration, reformulation and approximation, the modern tradition in Spain of the 1930s, It was considered one of the most decisive moments of architecture, where the architecture school had great significance. This was in addition to a modern architectural tradition that it had a development in the Basque country. While the economy and functionality requiring school buildings they were adequate to the Rationalist methodology.
In 1986 He obtained the Chair of architectural projects (III) in the school of architecture of Madrid.
The work of Fullaondo comprises more than one hundred projects on different architectural typologies and urban interventions, they are distributed throughout the Iberian Peninsula, especially in Bizkaia, What should add sculptures and paintings. Most of his works were performed in collaboration with other professionals, so that worked with around ninety colleagues. In fact Fullaondo met and was related to the main protagonists of the architecture of its time: architects, editors and historians, but also as with painters and sculptors. Fullaondo felt a special inclination towards the architecture of the modern movement, especially the work of Frank Lloyd Wright, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe and of Stijil group, that resulted in his work characterized by uneven and rhythmic geometry, Stressing the repetitive use of the sphere.
Chillida and Fullaondo collaborated repeatedly, as in the project not carried out to the lighthouse at the port of Bilbao in 1970, the architect described as the biggest failure of his professional life. Nor was the proposal to the Alhondiga Bilbao made in 1988 in collaboration with Oíza and Oteiza.
The economic crisis affecting the sector from mid-1970s, joined the political transition, they were difficult years. It was a time of solitude and meditation for Fullando, who already in the school of architecture, It adopted a path which he described as realistic or neorealista, alien to the trends that were being developed at the time, collaborating with other colleagues.
Reflection on the architecture and the arts was constant in the work of Fullaondo, It was also driven by his teaching activity. The result was thirty-nine books, and numerous articles in different magazines of the time, While his work was collected in bulletins of architecture throughout his professional career. One of his most important contributions was the magazine New form (1967- 1975), published in Madrid thanks to the financing of Juan Huarte constructor. The 111 issues of the newsletter became a reference for the architectural panorama and plastic of the moment. They paid special interest to the historical avant-gardes, especially in Spain, and its main protagonists. The cities of Madrid and Bilbao were also object of different studies, initiating a historiographic work pioneer, which developed in later works, especially about Bilbao. As a result his studies have become a point of reference for the study of contemporary Spanish architecture, the city and the architecture of Bilbao, or the sculpture of Oteiza and Chillida.
AWARDS AND awards.
Among the numerous awards and achievements by Juan Daniel Fullaondo, We will make mention of those most relevant:
- 1962 – National Architecture Award.
- 1963 – Vizcaya and Pedro Asua award.
- 1986 – Professor of architectural projects (III) in the school of architecture of Madrid.
-
Juan Daniel Pérez me – Studies Foundation